So let’s continue with the ancient Rome and sex
Virtus – male ideal in ancient Rome
Rome was an extremely masculine, or “macho” society. Unlike the Greek world, the Roman male ideal was based on the following pillars: virtue, masculine honor, self-discipline, humility, patriotism, family loyalty, and respect for ancestors. That was the virtue. This was in the tombs of the great families of Rome. In the ancient Greek world, predominantly sexual positions for women (retro, tergo – today’s doggy-style) were prevalent, whereas in the Roman era women preferred sedeo, incurvo.
Prostitution
Almost every ancient Roman city had a brothel. These usually worked legally, with the permission of the aedilis (“law enforcement officer”), and here the meretrixes (the “prostitute”) could work. Pompeii is the most well-known example of the everyday life of prostitution.
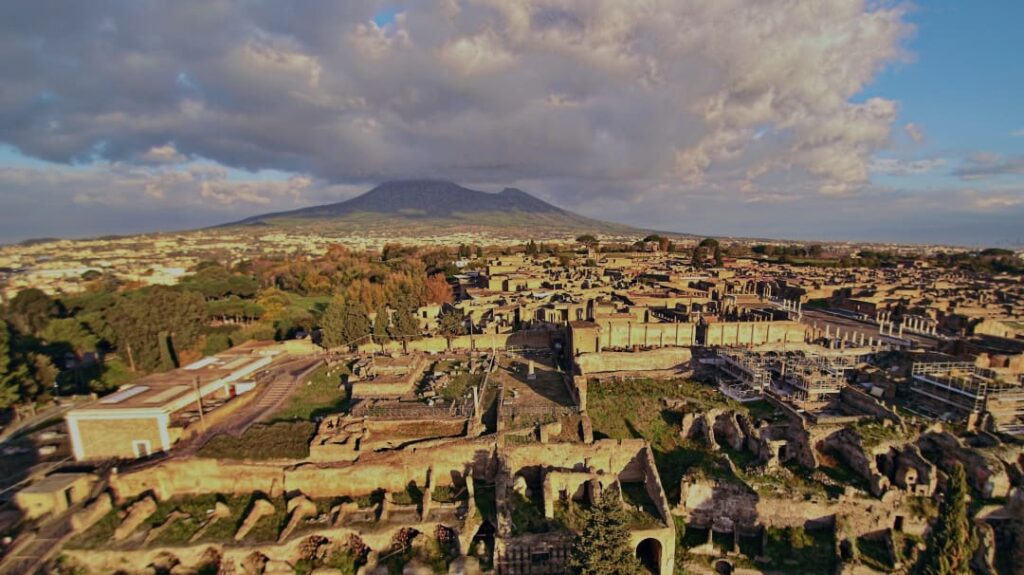

We know nearly a hundred prostitutes – men and women – for their names, services, “abilities” and prices. But there are many portrayals. Prostitution was legal, but there were strict rules: a Roman citizen could not be a prostitute, a married woman or a man could not prostitute. The meretrix had a specific toga (toga mulieris). Completely naked, they rarely depict women, most of them wearing a bra-like band.
However, there were tragedies in the lives of prostitutes. In 1912, the archaeologists discovered dozens of baby graves at a brothel. Archaeologists speculate that prostitutes had to kill their children.
Pederastics and adult love for men
The Romans, because of the main pillars of the Virtue, tolerated only certain forms of pederastics (an adult male’s erotic relationship with a 13-17-year-old boy). An adult Roman citizen could only sleep with a slave boy. But they accepted only the active role. The inclusive, passive role was unworthy of a Roman citizen. However, they suspected Marcus Antonius and many Roman emperors of taking a passive role. The best-known pederaster in the Roman world is related to the name of Emperor Hadrian and his lover, Antinous.
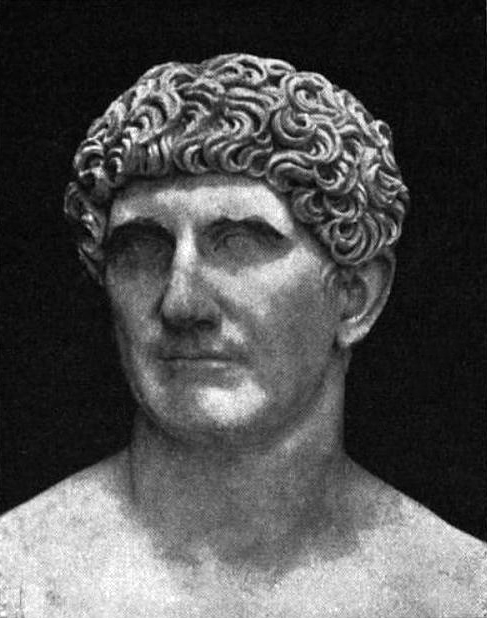

All forms of sexual relations between two Roman men have been prohibited by law in Rome since the Republic. But there are many “me too” stories from antiquity when prestigious Roman soldiers or citizens abused young boys or adult soldiers by abusing their power. One of the most scandalous cases is Gaius Lusius. He had been harassing Trebonius, a young man famous for his beauty, for a long time. The harassment resulted in a young soldier stabbing and killing Gaius Lucius one night. Then, in a lawsuit, he told the truth, and they honored him.
There are many erotic stories about the Roman emperors. Such as the “fish” (children) lurking in the Emperor’s Tiberius basin. Or the orgies of Caligula, Nero’s female attire, and her passive role in bed. Their credibility is rather uncertain. Because they were usually created after the death of emperors and were part of enduring campaigns.
Sex and archeology
The Romans’ sexual habits we know primarily from works of fiction. Besides that from imperial biographies, ancient dramas, and prose. However, there are numerous archaeological finds. Mainly from Pompeii and Herculanaeum. The archeology of the brothel houses and their rich source is outstanding. Phallic hangers and candlesticks were present in the houses mainly because of their magical power and protective role. The phallic columns and reliefs on the houses marked the brothel.
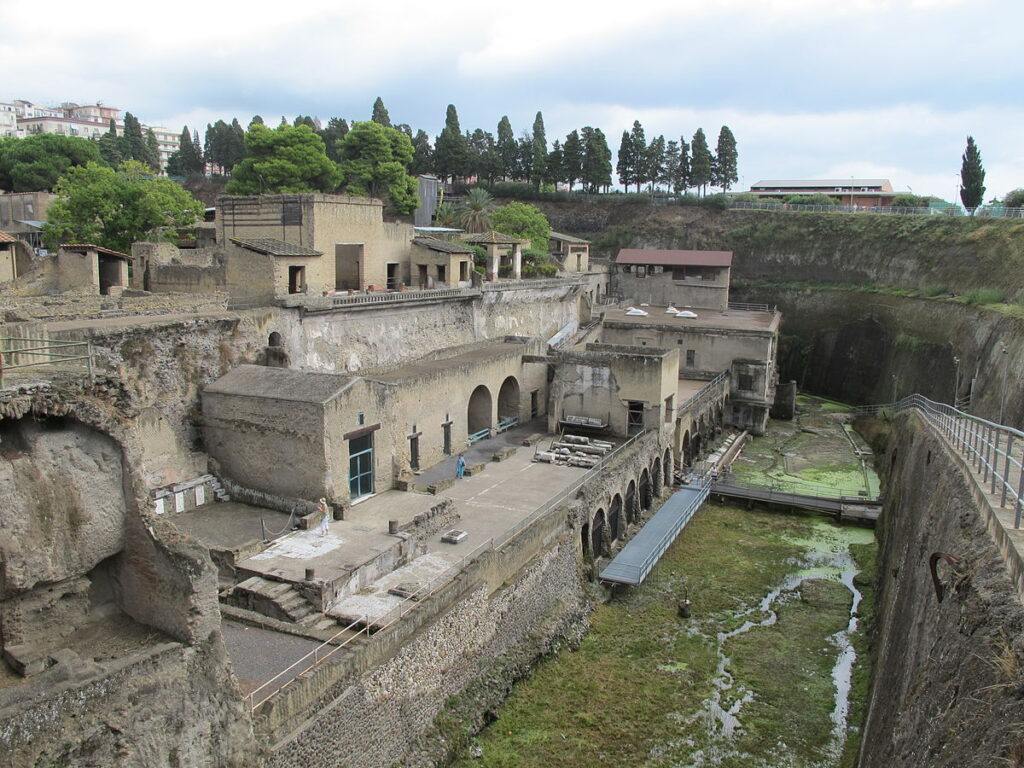

At the same time, brothels feature frescoes, special beds, depictions of women’s dresses, and even sexual aids (dildos). We know some of the Roman bronze vessels with erotic scenes. Some of the candlesticks and molds decorated with erotic scenes were funerary items. These were probably messages of lust and zeal for life.
The history of Roman sexuality is an extremely complex subject that fills libraries. But there are also some misconceptions. The history of Roman sexuality is often confused with the history of Greek sexuality. And they presented it in a much more liberal way than it was.
Read more about the ancient Rome in this article! And if you are interested in this topic – story of sex and eroticism -, then read about the ancient India and China, as well!